Fioricet can cause side effects that may impair your thinking or reactions. Be careful if you drive or do anything that requires you to be awake and alert.
Avoid drinking alcohol. It may increase your risk of liver damage while taking acetaminophen.
Mayne Pharma
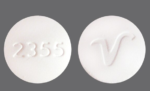
Pill Identification: MIA 110
Avoid taking Fioricet with medications that affect your concentration, such as other narcotic pain relievers, general anesthetics, sleeping pills, anti-allergy medications, sedative-hypnotics, and tranquilizers (such as chlordiazepoxide). These may cause further drowsiness.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using any other cold, allergy, pain, or sleep medication. Acetaminophen (sometimes abbreviated as APAP) is contained in many combination medicines. Taking certain products together can cause you to get too much acetaminophen which can lead to a fatal overdose. Check the label to see if a medicine contains acetaminophen or APAP.
While you are taking Fioricet, avoid taking diet pills, caffeine pills, or other stimulants (such as ADHD medications) without your doctor’s advice.
Do not use Fioricet if you have taken an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A dangerous drug interaction could occur. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, and tranylcypromine.
You should not use Fioricet if you are allergic to acetaminophen, butalbital, or caffeine, if you have porphyria, or if you have recently used alcohol, sedatives, tranquilizers, or other narcotic medications.
Fioricet interactions
- Some medicines can affect how this medicine works. Tell your doctor if you are also using an MAO inhibitor (MAOI).
- Tell your doctor if you use anything else that makes you sleepy. Some examples are allergy medicine, narcotic pain medicine, and alcohol.
- Do not drink alcohol while you are using this medicine. Acetaminophen can damage your liver, and alcohol can increase this risk.
- This medicine may make you dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive or do anything that could be dangerous until you know how this medicine affects you.
- This medicine can be habit-forming. Do not use more than your prescribed dose. Call your doctor if you think your medicine is not working.
- Tell any doctor or dentist who treats you that you are using this medicine. This medicine may affect certain medical test results.
- Keep all medicine out of the reach of children. Never share your medicine with anyone.
What Kinds of Foods I should Avoid while Taking Fioricet ?
Butalbital 50mg, Acetaminophen 300mg, Caffeine 40mg, Oral capsule
Alcohol
· Severity: Major
· Notes for Consumers: Do not drink alcohol while taking this medication. Drinking alcohol while taking this medication increases the risk of liver injury. Contact your care team right away if you experience right upper belly pain, loss of appetite, nausea, light-colored stool, dark yellow or brown urine, yellowing skin or eyes, or unusual weakness or fatigue.
· Notes for Professionals: The risk of developing hepatotoxicity from acetaminophen appears to be increased in patients who regularly consume alcohol. Patients who drink more than 3 alcohol-containing drinks a day and take acetaminophen are at increased risk of developing hepatotoxicity. Acute or chronic alcohol use increases acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inducing CYP2E1 leading to increased formation of the hepatotoxic metabolite of acetaminophen. Also, chronic alcohol use can deplete liver glutathione stores. Administration of acetaminophen should be limited or avoided altogether in patients with alcoholism or patients who consume alcohol regularly.
Butalbital 50mg, Acetaminophen 300mg, Caffeine 40mg, Oral capsule
Caffeine-containing Foods/Beverages
· Severity: Moderate
· Notes for Consumers: Caffeine may cause sleeplessness, so if you are taking a Barbiturate to help you sleep, you may wish to avoid taking caffeine and caffeine-containing foods like colas, coffee, teas, or chocolates within several hours prior to bedtime. Barbiturates may also decrease the actions of Caffeine; if you have a high intake of caffeinated foods or beverages you may experience a headache or irritability from decreased caffeine levels while taking these drugs until your body adjusts. If you take Caffeine for other purposes, notify your health care provider if you think Caffeine is not working as well for you.
· Notes for Professionals: Caffeine has been reported to increase the metabolism of barbiturates, and barbiturates increase caffeine elimination. Higher caffeine doses may be needed after barbiturate administration.
Butalbital 50mg, Acetaminophen 300mg, Caffeine 40mg, Oral capsule
Cannabis
· Severity: Major
· Notes for Consumers: Discuss cannabis use with your care team. The effects of cannabis may be altered if used with your medication. Call emergency services right away if you experience slow or shallow breathing, shortness of breath, feeling faint, dizziness, confusion, or trouble staying awake.
· Notes for Professionals: Advise patients to avoid cannabis use during barbiturate treatment due to the risk for additive CNS depression and other adverse reactions. Concomitant use may also decrease the concentration of some cannabinoids and alter their effects. The cannabinoids delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are CYP3A substrates and barbiturates are strong CYP3A inducers. Concomitant use of a cannabinoid product containing THC and CBD at an approximate 1:1 ratio with another strong CYP3A inducer decreased THC, 11-OH-THC, and CBD peak exposures by 36%, 87%, and 52% respectively.
Butalbital 50mg, Acetaminophen 300mg, Caffeine 40mg, Oral capsule
Grapefruit juice
· Severity: Mild
· Notes for Consumers: Do not significantly alter your grapefruit juice intake while taking medicines containing caffeine. Some reports suggest that intake of grapefruit juice can increase side effects from caffeine. Too much Caffeine can cause effects like nausea, tremor, nervousness, or sleeplessness. If these occur, consider ingesting less caffeine daily.
· Notes for Professionals: Data are limited and conflicting as to whether grapefruit juice significantly alters the serum concentrations and/or AUC of caffeine. Caffeine is primarily a CYP1A2 substrate, and grapefruit juice appears to have but a small effect on this enzyme in vivo. One report suggests that grapefruit juice decreases caffeine elimination by inhibition of flavin-containing monooxygenase, a P450 independent system. This interaction might increase caffeine levels and mildly potentiate the clinical effects and common side effects of caffeine. If side effects appear, patients may need to limit either caffeine or grapefruit juice intake.
Butalbital 50mg, Acetaminophen 300mg, Caffeine 40mg, Oral capsule
Tobacco
· Severity: Major
· Notes for Consumers: Do not smoke or use tobacco products while taking this medication. When used together, your medication may not work as well for you.
· Notes for Professionals: Advise patients who are taking caffeine to avoid smoking tobacco. Smoking tobacco has been observed to increase caffeine clearance by 50% to 70%. Caffeine is a CYP1A2 substrate and smoking tobacco induces CYP1A2.
Pain Medications, Pain Relief, and Pain Management