Gabapentin capsules are available under different trade names and at different strengths. Gabapentin is used most commonly to treat epilepsy and neuropathic, or nerve, pain. The trade names of gabapentin capsules depend on the country in which they are manufactured and the manufacturer. The doctor will prescribe the correct dose of gabapentin according to the clinical indication.
Gabapentin comes as:
- 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules
- 300 mg, 600 mg, and 800 mg tablets
- a 250 mg/5 mL oral (by mouth) solution.
Inactive ingredients in the capsules include lactose, cornstarch, and talc.
- The 100-mg capsule shell also contains: gelatin and titanium dioxide.
- The 300-mg capsule shell also contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
- The 400-mg capsule shell also contains: gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The imprinting ink contains FD&C Blue No. 2 and titanium dioxide.
Inactive ingredients in the tablets include poloxamer 407, copolyvidonum, cornstarch, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, candelilla wax, and purified water.
Inactive ingredients in the oral solution include glycerin, xylitol, purified water, and artificial flavor.

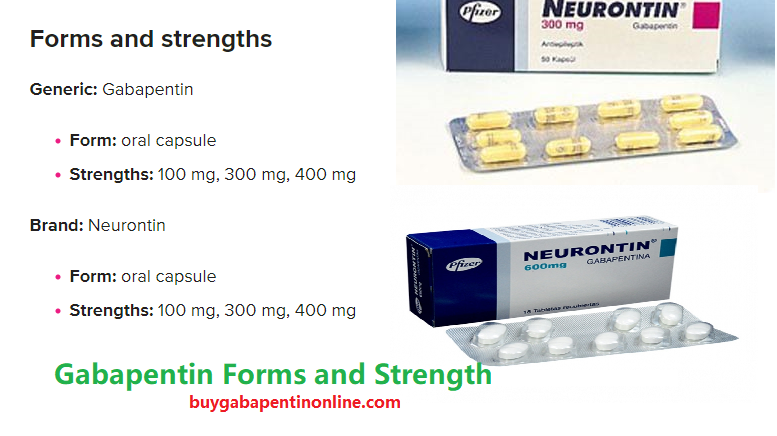
Forms and strengths
Generic: Gabapentin
- Form: oral capsule
- Strengths: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg
Brand: Neurontin
- Form: oral capsule
- Strengths: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg
Forms and strengths
Generic: Gabapentin
- Form: oral capsule
- Strengths: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg
Brand: Neurontin
- Form: oral capsule
- Strengths: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg
Dosage for postherpetic neuralgia
Adult dosage (ages 18–64 years)
- Typical starting dosage: Day 1, 300 mg; day 2, 600 mg (300 mg two times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day); day 3, 900 mg (300 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day). Your doctor may further increase your dosage after day 3.
- Maximum dosage: 1,800 mg per day (600 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day)
Child dosage (ages 0–17 years)
Dosage for people younger than 18 years has not been established.
Senior dosage (ages 65 years and older)
Your kidney function may decrease with age. Your body may get rid of this drug more slowly. Your doctor may start you on a lower dose so that too much of this drug does not build up in your body. Too much of the drug in your body can be dangerous. Your doctor may change your dose based on how well your kidneys are working.
Dosage for partial-onset seizures
Adult dosage (ages 18–64 years)
Typical starting dosage: 900 mg per day (300 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day). Your doctor may increase your dose to 2,400–3,600 mg per day.
Child dosage (ages 12–17 years)
Typical starting dosage: 300 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day. This can increase to 2,400–3,600 mg per day.
Child dosage (ages 3–11 years)
Typical starting dosage: 10–15 mg/kg/day, divided into three doses, spaced evenly throughout the day. Your child’s doctor may increase the dosage to meet your child’s needs.
Maximum dosage: 50 mg/kg/day.
Child dosage (ages 0–2 years)
Dosage for people younger than 3 years has not been established.
Senior dosage (ages 65 years and older)
Your kidney function may decrease with age. Your body may get rid of this drug more slowly. Your doctor may start you on a lower dose so that too much of this drug does not build up in your body. Too much of the drug in your body can be dangerous. Your doctor may change your dose based on how well your kidneys are working.
Special considerations
Kidney problems: If you are older than 12 years and have kidney problems or are on hemodialysis, your dose of gabapentin will need to be changed. This will be based on how well your kidneys are working.
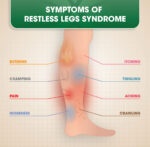
Pain Medications, Pain Relief, and Pain Management