Fibromyalgia is a complex chronic pain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, predominantly women.
The condition is characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tenderness in localized areas of the body.
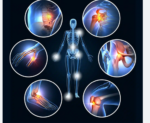
The pain associated with fibromyalgia is typically described as a deep, dull ache that is present throughout the body, particularly in the muscles, joints, and soft tissues. The pain can be exacerbated by physical activity, stress, and changes in weather or temperature.
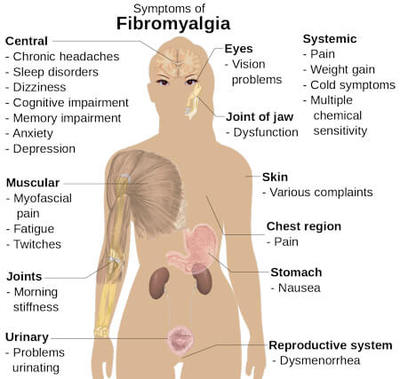
What is the Symptoms of Fibromyalgia ?
The symptoms of fibromyalgia can vary in intensity and may come and go over time. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Widespread Pain: The hallmark symptom of fibromyalgia is widespread pain, which can be described as a deep, dull ache that is present throughout the body, particularly in the muscles, joints, and soft tissues. The pain can be exacerbated by physical activity, stress, and changes in weather or temperature.
- Fatigue: People with fibromyalgia often feel exhausted, even after a full night’s sleep, and may have difficulty performing daily activities.
- Sleep Disturbances: Fibromyalgia can cause a variety of sleep disturbances, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, restless legs syndrome, and sleep apnea. People with fibromyalgia may also wake up feeling unrefreshed.
- Cognitive Difficulties: Some people with fibromyalgia may experience cognitive difficulties, sometimes referred to as “fibro fog.” This can include problems with memory, concentration, and mental clarity.
- Headaches: Fibromyalgia can cause headaches, including tension headaches and migraines.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Many people with fibromyalgia also experience symptoms of IBS, including abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Sensitivity to Touch: People with fibromyalgia may be more sensitive to touch than others, particularly in areas of the body that are affected by the condition. This can make even light pressure or touch painful.
- Stiffness: Fibromyalgia can cause stiffness, particularly in the morning or after sitting or standing for long periods of time.
- Depression and Anxiety: Fibromyalgia can cause or worsen depression and anxiety, which can further affect a person’s quality of life.
- Tender Points: These are localized areas of the body that are sensitive to pressure, such as the back of the neck, shoulders, chest, hips, and knees. Tender points can be painful to the touch and may be used to help diagnose fibromyalgia.
It’s important to note that everyone with fibromyalgia may experience symptoms differently, and symptoms can vary in severity from person to person. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is the Reasons of Fibromyalgia?
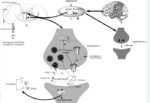
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not known, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
- Genetic Factors: Research suggests that fibromyalgia may have a genetic component, as the condition tends to run in families. Studies have identified specific genetic variations that may increase a person’s risk of developing fibromyalgia.
- Environmental Factors: Fibromyalgia may be triggered or exacerbated by certain environmental factors, such as physical or emotional trauma, infections or illnesses, and exposure to toxins or pollutants.
- Psychological Factors: People with fibromyalgia often have comorbid psychological conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Stress and emotional trauma can also trigger or worsen fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Central Nervous System Abnormalities: Researchers believe that fibromyalgia may be caused by abnormalities in the central nervous system that affect the way the brain processes pain signals. In people with fibromyalgia, the brain appears to amplify pain signals, making them more intense and difficult to tolerate.
It’s important to note that while these factors may increase a person’s risk of developing fibromyalgia, they do not necessarily cause the condition. The exact mechanisms behind fibromyalgia are still being studied, and more research is needed to fully understand the condition.
How to Treat Fibromyalgia?
There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the symptoms of the condition. Treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach that addresses the various symptoms of the condition. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
- Medications: There are several medications that can be used to treat fibromyalgia, including pain relievers, antidepressants, and sleep aids. Pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help to reduce pain and inflammation. Antidepressants such as duloxetine and milnacipran can help to reduce pain and improve sleep. Sleep aids such as zolpidem and eszopiclone may help to improve sleep quality.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help to reduce pain and improve overall function in people with fibromyalgia. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are often recommended. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise over time.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve mobility and reduce pain in people with fibromyalgia. A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program to help strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a form of talk therapy that can help to reduce the emotional impact of fibromyalgia and improve coping skills. CBT can help people with fibromyalgia to manage stress, reduce anxiety and depression, and improve sleep quality.
- Stress Management: Stress can worsen fibromyalgia symptoms, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress. This may include relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, as well as lifestyle changes such as reducing workload or adjusting expectations.
- Dietary Changes: Some people with fibromyalgia find that dietary changes can help to reduce symptoms. This may include avoiding certain foods or ingredients, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods, and increasing intake of nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Alternative Therapies: Some people with fibromyalgia find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care. While the evidence for the effectiveness of these therapies is limited, they may be helpful for some people.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific symptoms of fibromyalgia. With the right combination of treatments, many people with fibromyalgia are able to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach that addresses the various symptoms of the condition. This may include medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and sleep aids, as well as lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress-management techniques, and dietary modifications.
Overall, fibromyalgia can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right combination of treatments, many people are able to improve their symptoms and quality of life.

What are the Medicines for Fibromyalgia ?
There are several medications that can be used to treat the symptoms of fibromyalgia. These include:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be helpful in reducing mild to moderate pain associated with fibromyalgia.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as duloxetine and milnacipran, can help to reduce pain and improve mood in people with fibromyalgia. These medications work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain that regulate pain and mood.
- Anti-seizure medications: Certain anti-seizure medications, such as gabapentin and pregabalin, can help to reduce pain and improve sleep in people with fibromyalgia. These medications work by regulating the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain that are involved in pain perception.
- Muscle relaxants: Muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine may be helpful in reducing muscle spasms and improving sleep in people with fibromyalgia.
- Sleep aids: Sleep disturbances are common in people with fibromyalgia, and certain sleep aids such as zolpidem and eszopiclone may be helpful in improving sleep quality.
It’s important to note that medication treatment for fibromyalgia should be individualized and tailored to the specific symptoms and needs of the patient. Some medications may not work for everyone, and there may be side effects associated with certain medications. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for fibromyalgia.
Pain Medications, Pain Relief, and Pain Management