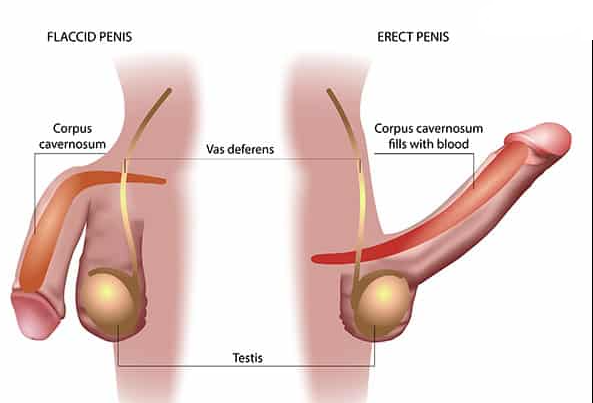
What is erectile dysfunction?
The malady formerly known as impotence, erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to get or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfying sex. That might include erections that don’t last as long as you want or aren’t as firm as you’d like. ED is very prevalent among American men: Experts estimate that more than 30 million American men have experienced these kinds of erection issues (Nunes, 2012).
How common is erectile dysfunction?
Approximately one in 10 adult males will suffer from ED on a long-term basis.
Many men do experience occasional failure to achieve erection, which can occur for a variety of reasons, such as drinking too much alcohol, stress, relationship problems, or from being extremely tired.
The failure to get an erection less than 20% of the time is not unusual and typically does not require treatment. However, the failure to achieve an erection more than 50% of the time generally means that there is a problem and treatment is needed.
ED does not have to be a part of getting older. While it is true that some older men may need more stimulation, they should still be able to achieve an erection and enjoy intercourse.
What Is the Erectile dysfunction Medications ?
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, can affect your quality of life by decreasing your satisfaction from sex. ED can have many causes, both psychological and physical. ED from physical causes is fairly common in men as they age. Medications are available that can help treat ED for many men.

The most well-known ED medications include:
These prescription drugs increase the levels of nitric oxide in your blood. Nitric oxide is a vasodilator, meaning it makes your blood vessels widen to help increase the blood flow. These drugs are especially effective at widening the blood vessels in your penis. More blood in your penis makes it much easier for you to get and maintain an erection when you are sexually aroused.
How is erectile dysfunction (ED) diagnosed?
Because there are a variety of causes for ED, there are several different tests your doctor may use to diagnose the condition and determine its cause. Only after the cause of ED is determined can it be effectively treated.
Before ordering any tests, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a thorough physical examination. The doctor will also “interview” you about your personal and sexual history. Some of these questions will be very personal and may feel intrusive. However, it is important that you answer these questions honestly. The questions asked may include:
- What medications or drugs are you currently using? This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs, herbals, dietary supplements and illegal drugs.
- Have you had any psychological problems such as stress, anxiety and depression?
- When did you first notice symptoms of ED?
- What are the frequency, quality and duration of any erections you have had?
- What are the specifics of the circumstances under which ED first occurred?
- Do/did you experience erections at night or during the morning?
- What sexual techniques do you use?
- Are there problems in your current relationship?
The doctor may also wish to interview your sexual partner since your partner may be able to offer in sight about the underlying causes.
After your physical examination and discussion, your doctor may then order any one of the following tests to further diagnose your condition:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This is a set of blood tests that, among other things, can detect the presence of anemia. Anemia is caused by a low red blood cell count and can cause fatigue, which in turn can cause ED.
- Liver and kidney function tests: These blood tests may indicate whether ED may be due to your kidneys or liver functioning improperly.
- Lipid profile: This blood test measures the level of lipids (fats), like cholesterol. High levels may indicate atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can affect blood circulation in the penis.
- Thyroid function test: One of the thyroid hormones’ functions is to regulate the production of sex hormones, and a deficiency in these hormones may contribute to or cause ED.
- Blood hormone studies: Testosterone and/or prolactin levels in the blood may be measured to see if abnormalities in either of these sex hormones are present.
- Urinalysis: Analysis of urine can provide a wealth of information, including information on protein, sugar and testosterone levels. Abnormal measurements of these substances can indicate diabetes, kidney disease or a testosterone deficiency, all which can cause ED.
- Duplex ultrasound: This is perhaps the best test for evaluating ED. An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to take “pictures” of the body’s tissues. For people with ED, an ultrasound may be used to evaluate blood flow and check for signs of a venous leak, atherosclerosis (hardening of arteries) or tissue scarring. This test is performed both while the penis is erect (usually induced by an injection of a drug that stimulates erection) and also while it is soft.
- Bulbocavernosus reflex: This test evaluates nerve sensation in the penis. During the test, your doctor will squeeze the head of your penis, which should immediately cause your anus to contract. If nerve function is abnormal, there will be a delay in response time.
- Nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT): This test measures a man’s erectile function while he is sleeping. Normally, a man will have five or six erections while asleep. A lack of these erections may indicate there is a problem with nerve function or circulation to the penis. The test uses two methods, the snap gauge method and the strain gauge method. The snap gauge method is performed by wrapping three plastic bands of varying strength around the penis. Erectile function is then measured based on which of the three bands breaks. The strain gauge method works by placing elastic bands around the tip and base of the penis. If the penis becomes erect during the night, the bands stretch, measuring the changes in penile circumference.
- Penile biothesiometry: This test involves the use of electromagnetic vibration to determine sensitivity and nerve function. A decreased sensitivity to these vibrations may indicate nerve damage.
- Vasoactive injection: During this test, an erection is produced by injecting special solutions that cause the blood vessels to dilate (enlarge) allowing blood to enter the penis.
- Dynamic infusion cavernosometry: This test is used for men with ED who have a venous leak. During this test, fluid is pumped into the penis at a predetermined rate. By measuring the rate at which fluid must be pumped to attain a rigid erection, doctors can determine the severity of the venous leak.
- Cavernosography: Used in conjunction with the dynamic infusion cavernosometry, this test involves injecting a dye into the penis. The penis is then X-rayed so that the venous leak can be seen.
- Arteriography: This test is given to people who are candidates for vascular reconstructive surgery. A dye is injected into the artery believed to be damaged and X-rays will be taken.
Before you are given any of these tests, your doctor will explain what is involved. If you have any questions, do not hesitate to ask your doctor.
However, these drugs can also cause side some effects.
Here are seven of the most common side effects from ED medications:

Headaches
Headaches are the most common side effect associated with ED medications. The sudden change in blood flow from the increased levels of nitric oxide causes the headaches.
This side effect is common with all forms of ED medications, so switching brands won’t necessarily alleviate your symptoms. If you have headaches from your ED drug, talk to your doctor about how to prevent them.
Body aches and pains
Some people have muscle aches and pains throughout their bodies while taking ED medications. Others have reported specific pain in their lower back. If you have these types of pain while taking ED medication, over-the-counter (OTC) pain medication may help.
However, you should talk to your doctor about other possible causes of your pain. Your doctor can help you choose an OTC medication that is safe to take with your ED medications and with any other medications you take.
Digestive system problems
Your ED medication may cause uncomfortable digestive system side effects. The most common are indigestion and diarrhea.
To help relieve minor problems, consider making dietary changes to reduce upset stomach. Drinking water instead of caffeinated beverages, alcohol, or juice may help. If changing your diet doesn’t work, talk to your doctor about OTC remedies that may help.
Dizziness
An increase in nitric oxide can cause some men to become dizzy. The dizziness caused by ED medications is generally mild. However, any dizziness can cause discomfort during everyday activities.
In rare cases, dizziness from ED medications has led to fainting, which can become a serious health issue. You should tell your doctor if you experience dizziness while taking ED medications. If you faint while taking these medications, see your doctor right away.
Vision changes
ED medications can change the way you see things — literally. They can temporarily alter your eyesight and even cause blurry vision. ED medications aren’t recommended if you have had vision loss, or a retinal disorder called retinitis pigmentosa.
A complete loss of vision or changes that don’t go away can signify a more serious issue with your ED medication. Seek emergency medical care if you experience these symptoms.
Flushes
Flushes are temporary periods of redness of the skin. Flushes usually develop on your face and may also spread to parts of your body. Flushes can be mild, like blotchy skin, or severe, like rashes. Although the appearance may make you uncomfortable, flushes typically aren’t harmful.
Flushes from ED medications may get worse when you:
- eat hot or spicy foods
- drink alcohol
- are outside in warm temperatures
Congestion and runny nose
Congestion or a runny or stuffy nose can be a common symptom of ED medications. In most cases, these side effects go away without treatment. Talk to your doctor if they persist.
Minor side effects are common when taking ED medication. Still, there are a few side effects that aren’t as common, and some can even be dangerous. Severe side effects of ED medications can include:
- priapism (erections that last longer than 4 hours)
- sudden changes in hearing
- vision loss
Contact your doctor immediately if you have any of these severe side effects.
Certain men are more at risk of these side effects than others. This may be because of other conditions they have or other medications they take.
Serious side effects of ED medication
Go to the emergency room immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or side effects:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Severe headaches
- Fainting
- Erections that last longer than four hours
- Visual changes (like loss of sight)
- Or anything out of the ordinary—even lightheadedness
If you notice any severe or prolonged symptoms at all, contact a healthcare provider immediately. It doesn’t matter how rare a side effect is if you’re the one experiencing it.
When discussing ED treatment with your doctor, it’s important to tell them about all drugs that you take and other health conditions you have. If ED drugs aren’t right for you, your doctor may suggest other treatment options, such as surgery or vacuum pumps.
Pain Medications, Pain Relief, and Pain Management