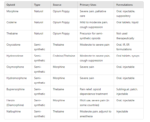
- Acetaminophen with codeine (Tylenol #2, #3, #4)
- Buprenorphine (Butrans)
- Fentanyl transdermal patches (Duragesic)
- Hydrocodone with acetaminophen (Lortab Elixir, Vicodin)
- Hydrocodone with ibuprofen (Vicoprofen)
- Hydrocodone (Zohydro)
- Hydromorphone (Exalgo)
- Meperidine (Demerol, Merpergan)
- Methadone (Dolophine)
- Morphine and morphine sustained release (MS-Contin, Avinza, Kadian)
- Oxycodone sustained release (OxyContin)
- Oxycodone with acetaminophen (Percocet)
- Oxycodone with aspirin (Percodan)
- Oxycodone with ibuprofen (Combunox)
- Oxymorphone (Opana, Opana ER)
- Pentazocine (Talwin,)
- Propoxyphene with aspirin, propoxyphene with acetaminophen
- Tapentadol (Nucynta, Nucynta ER)
- Tramadol, tramadol with acetaminophen (Ultram, Ultracet)
Opioid Analgesics

- Abstral
- Actiq
- Astramorph
- Buprenex
- buprenorphine
- buprenorphine transdermal
- butorphanol
- Butrans
- codeine
- ConZip
- Demerol
- Depodur
- Dilaudid
- Dilaudid-HP
- Dolophine
- Dsuvia
- Duragesic
- Duramorph
- Exalgo
- fentanyl
- fentanyl intranasal
- fentanyl iontophoretic transdermal system
- fentanyl transdermal
- fentanyl transmucosal
- Fentora
- hydrocodone
- hydromorphone
- Hysingla ER
- Infumorph
- Ionsys
- Kadian
- Lazanda
- Levo Dromoran
- levorphanol
- loxicodegol
- meperidine
- methadone
- Methadose
- Mitigo
- MorphaBond
- morphine
- MS Contin
- nalbuphine
- Nubain
- Nucynta
- Nucynta ER
- oliceridine
- Olinvyk
- Onsolis
- Opana
- Oxaydo
- oxycodone
- oxycodone/naloxone
- oxycodone/naltrexone
- OxyContin
- oxymorphone
- pentazocine
- pethidine
- Qdolo
- remifentanil
- Roxicodone
- RoxyBond
- Stadol
- Sublimaze
- Subsys
- Sufenta
- sufentanil
- sufentanil SL
- Talwin
- tapentadol
- Targiniq ER
- tramadol
- Troxyca ER
- Ultiva
- Ultram
- Vantrela ER
- Xtampza ER
- Zohydro ER
USE OPIOIDS SAFELY: 3 KEY STEPS
- Keep your doctor informed. Inform your health care professional about any past history of substance abuse. All patients treated with opioids for pain require careful monitoring by their health care professional for signs of abuse and addiction, and to determine when these analgesics are no longer needed.
- Follow directions carefully. Opioids are associated with significant side effects, including drowsiness, constipation, and depressed breathing depending on the amount taken. Taking too much could cause severe respiratory depression or death. Do not crush or break pills. This can alter the rate at which the medication is absorbed and lead to overdose and death.
- Reduce the risk of drug interactions. Don’t mix opioids with alcohol, antihistamines, barbiturates, or benzodiazepines. All of these substances slow breathing and their combined effects could lead to life-threatening respiratory depression.
Pain Medications, Pain Relief, and Pain Management